本文最后更新于:2023年11月8日 中午
WinMain函数参数介绍
int WINAPI WinMain(
HINSTANCE hInstance, // handle to current instance
HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, // handle to previous instance
LPSTR lpCmdLine, // command line
int nCmdShow // show state
);
WinMain函数接收4个参数,这些参数都是在系统调用WinMain函数时,传递给应用程序的。
第一个参数hInstance表示该程序当前运行的实例的句柄,这是一个数值。当程序在Windows下运行时,它唯一标识运行中的实例(注意,只有运行中的程序实例,才有实例句柄)。一个应用程序可以运行多个实例,每运行一个实例,系统都会给该实例分配一个句柄值,并通过hInstance参数传递给WinMain函数。
第二个参数hPrevInstance表示当前实例的前一个实例的句柄。通过查看MSDN我们可以知道,在Win32环境下,这个参数总是NULL,即在Win32环境下,这个参数不再起作用。
第三个参数lpCmdLine是一个以空终止的字符串,指定传递给应用程序的命令行参数。例如:在D盘下有一个sunxin.txt文件,当我们用鼠标双击这个文件时将启动记事本程序(notepad.exe),此时系统会将D:\sunxin.txt作为命令行参数传递给记事本程序的WinMain函数,记事本程序在得到这个文件的全路径名后,就在窗口中显示该文件的内容。要在VC++开发环境中向应用程序传递参数,可以单击菜单【Project】→【Settings】,选择“Debug”选项卡,在“Program arguments”编辑框中输入你想传递给应用程序的参数。
第四个参数nCmdShow指定程序的窗口应该如何显示,例如最大化、最小化、隐藏等。这个参数的值由该程序的调用者所指定,应用程序通常不需要去理会这个参数的值。
解题
首先对WinMain进行分析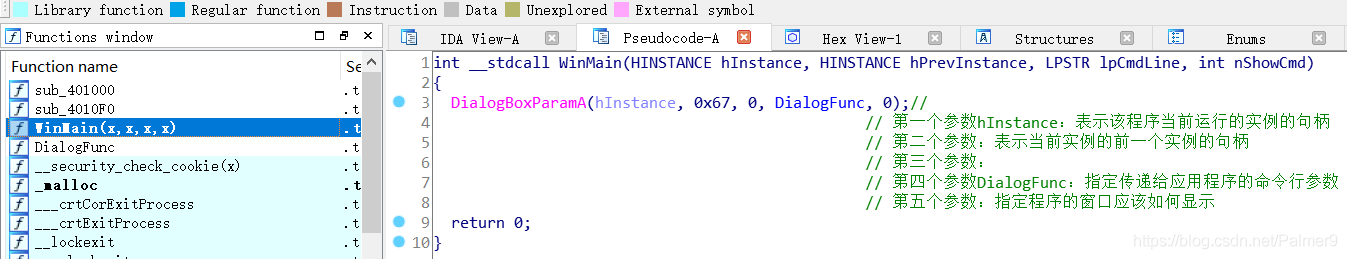
查看DialogFunc参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| BOOL __stdcall DialogFunc(HWND hDlg, UINT a2, WPARAM a3, LPARAM a4)
{
const char *v4; // esi
const char *v5; // edi
int v7[11]; // [esp+8h] [ebp-20030h]
CHAR String[9]; // [esp+34h] [ebp-20004h]
CHAR v9[3]; // [esp+10034h] [ebp-10004h]
if ( a2 == 272 )
return 1;
if ( a2 != 273 )
return 0; //
// a2 = 273
if ( a3 == 1001 ) // a3 = 1001
{
memset(String, 0, 0xFFFFu); // 给string清零
GetDlgItemTextA(hDlg, 1000, String, 0xFFFF);// 获取对话框文本,然后赋值给string
if ( strlen(String) == 8 ) // string的长度要为8
{
v7[0] = 90;
v7[1] = 74;
v7[2] = 83;
v7[3] = 69;
v7[4] = 67;
v7[5] = 97;
v7[6] = 78;
v7[7] = 72;
v7[8] = 51;
v7[9] = 110;
v7[10] = 103;
sub_4010F0(v7, 0, 10); // 对v7进行处理,处理后的数据
// 51 67 69 72 74 78 83 90 97 103 110
memset(v9, 0, 0xFFFFu); // 给v16清零
v9[0] = String[5];
v9[2] = String[7];
v9[1] = String[6];
v4 = sub_401000(v9, strlen(v9)); // 对v9进行base64加密然后传递给v4
memset(v9, 0, 0xFFFFu); // 给v9清零
v9[1] = String[3];
v9[0] = String[2];
v9[2] = String[4];
v5 = sub_401000(v9, strlen(v9)); // 对v9进行base64加密然后传递给v4
if ( String[0] == v7[0] + 34 // string[0] =
&& String[1] == v7[4] // string[1] =
&& 4 * String[2] - 141 == 3 * v7[2] // string[2] =
&& String[3] / 4 == 2 * (v7[7] / 9) // string[3] =
&& !strcmp(v4, "ak1w") // v4 = "ak1w"
&& !strcmp(
v5, // v5 = "V1Ax"
"V1Ax") )
{
MessageBoxA(hDlg, "U g3t 1T!", "@_@", 0);
}
}
return 0;
}
if ( a3 != 1 && a3 != 2 )
return 0;
EndDialog(hDlg, a3);
return 1;
}
|
其中sub_4010F0函数参数已知,可以直接求出其处理结果
转换为C语言脚本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int __cdecl sub_4010F0(int *a1, int a2, int a3)
{
int result;
int i;
int v5;
int v6;
result = a3;
for ( i = a2; i <= a3; a2 = i )
{
v5 = i;
v6 = a1[i];
if ( a2 < result && i < result )
{
do
{
if ( v6 > a1[result] )
{
if ( i >= result )
break;
++i;
a1[v5] = a1[result];
if ( i >= result )
break;
while ( a1[i] <= v6 )
{
if ( ++i >= result )
goto LABEL_13;
}
if ( i >= result )
break;
v5 = i;
a1[result] = a1[i];
}
--result;
}
while ( i < result );
}
LABEL_13:
a1[result] = v6;
sub_4010F0(a1, a2, i - 1);
result = a3;
++i;
}
return result;
}
int main()
{
int v7[11]={90,74,83,69,67,97,78,72,51,110,103};
sub_4010F0(v7,0,10);
for(int i=0;i<11;i++)
{
printf("%c ", v7[i]);
}
return 0;
}
|
得到如下结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| // a1 为 v7对应地址
// a2 = 0
// a3 = 10
int __cdecl sub_4010F0(int *a1, int a2, int a3)
{
int result; // eax
int i; // esi
int v5; // ecx
int v6; // edx
result = a3; // result = 10
for ( i = a2; i <= a3; a2 = i ) // i=0;i<=10;a2=i
{
v5 = i;
v6 = a1[i]; // 遍历a1对应地址的元素
if ( a2 < result && i < result ) // a2<10 并且 i<10
{
do
{
if ( v6 > a1[result] ) // 如果a1[i] > a1[result]
{
if ( i >= result )
break; // 如果i>=result则退出循环
++i; // 给i+1
a1[v5] = a1[result]; // 让a1[1] = a1[result]
if ( i >= result )
break; // 如果i>=result则退出循环 重复
while ( a1[i] <= v6 ) // 当a1[i] <= v6 此循环一定成立
{
if ( ++i >= result ) // 如果i = result - 1
goto LABEL_13;
}
if ( i >= result )
break;
v5 = i;
a1[result] = a1[i];
}
--result; // result减一
}
while ( i < result );
}
LABEL_13:
a1[result] = v6; // 让a1[result] = 之前的a1[i]
sub_4010F0(a1, a2, i - 1); // 进行递归……
result = a3;
++i;
}
return result;
}
|
对两个比较的字符串分别进行base64解密(byte内有明显的base64加密提示)
开头两个字符分别对应的是’3’+34后的字’U’,和对应栈内v7[4]=’J’
得到
